Figure 1
Download original image
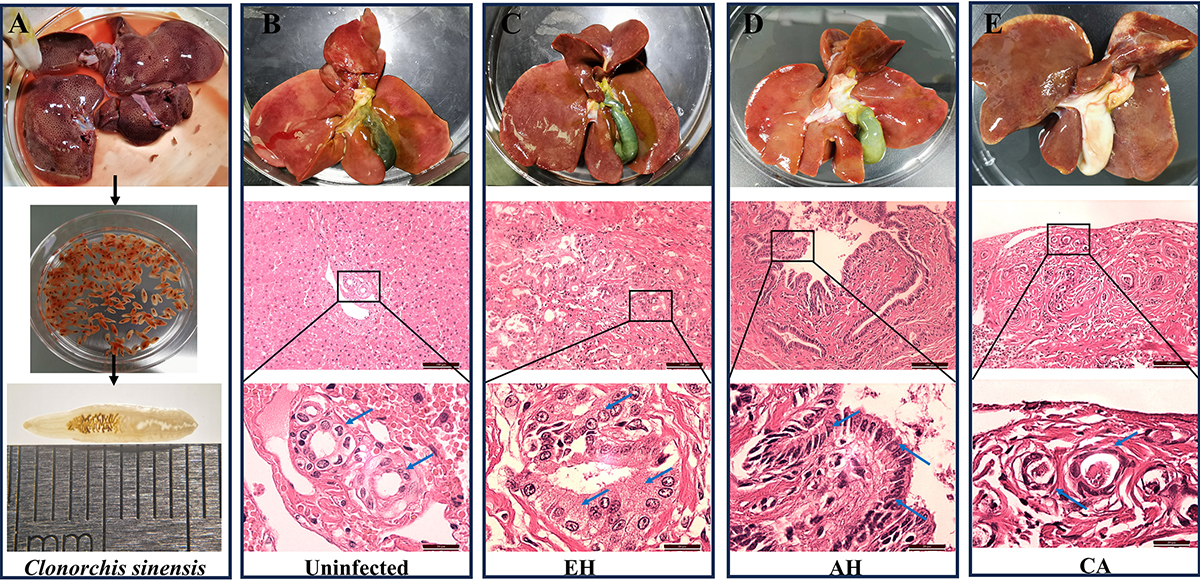
Histological examinations using hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining to observe the impact of C. sinensis infection on feline bile duct epithelium. A: Intravital collection and morphological observation of C. sinensis. B: HE staining of intrahepatic bile duct tissue from the uninfected group. C, D, and E present the HE staining analysis of intrahepatic bile duct tissues from cats infected with C. sinensis, illustrating epithelial hyperplasia (EH), adenomatous hyperplasia (AH), and carcinoma (CA), respectively. The blue arrows in panels C, D, and E point to the typical bile duct cells under various pathological conditions within the intrahepatic bile duct tissue.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


