Figure 9
Download original image
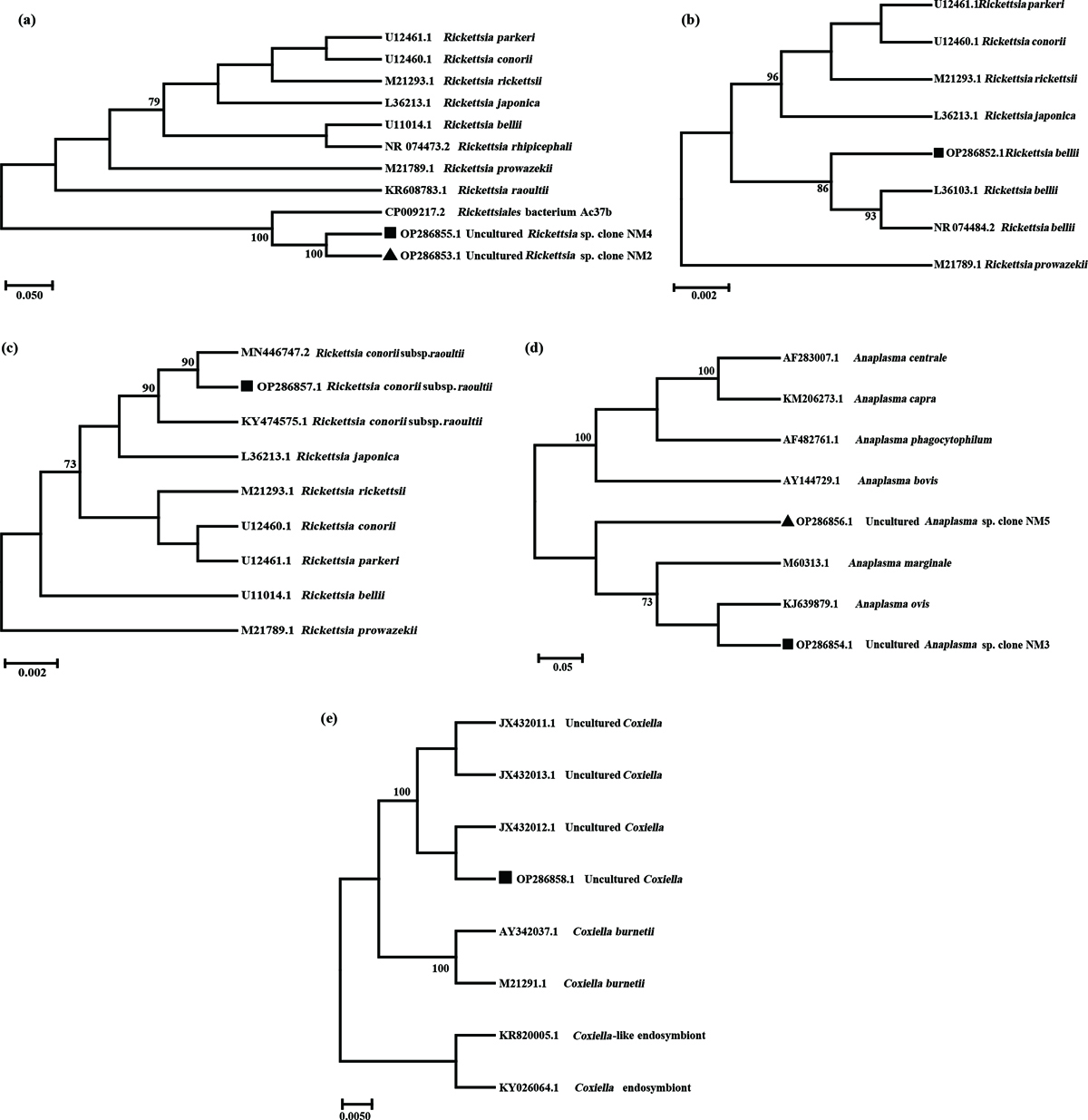
Phylogenetic tree of Rickettsiales bacterium Ac37b, Rickettsia bellii, Rickettsia raoultii, Anaplasma and Coxiella in ticks based on neighbor-joining (NJ) modeling; only values higher than 60 were added to the tree branches. (a) Phylogenetic tree of Rickettsiales bacterium Ac37b identified in Inner Mongolia; the 16S rRNA gene sequences obtained in this study are marked with black squares (1320 bp) and triangles (1430 bp). (b) Phylogenetic tree of Rickettsia bellii identified in Inner Mongolia; the 16S rRNA gene sequences obtained in this study are marked with black squares (1109 bp). (c) Phylogenetic tree of Rickettsia raoultii identified in Inner Mongolia; the 16S rRNA gene sequences obtained in this study are marked with black squares (855 bp). (d) Phylogenetic tree of Anaplasma identified in Inner Mongolia; the 16S rRNA gene sequences obtained in this study are marked with black squares (1455 bp) and triangles (547 bp). (e) Phylogenetic tree of Coxiella identified in Inner Mongolia; the 16S rRNA gene sequences obtained in this study are marked with black squares (1463 bp).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


