Figure 6
Download original image
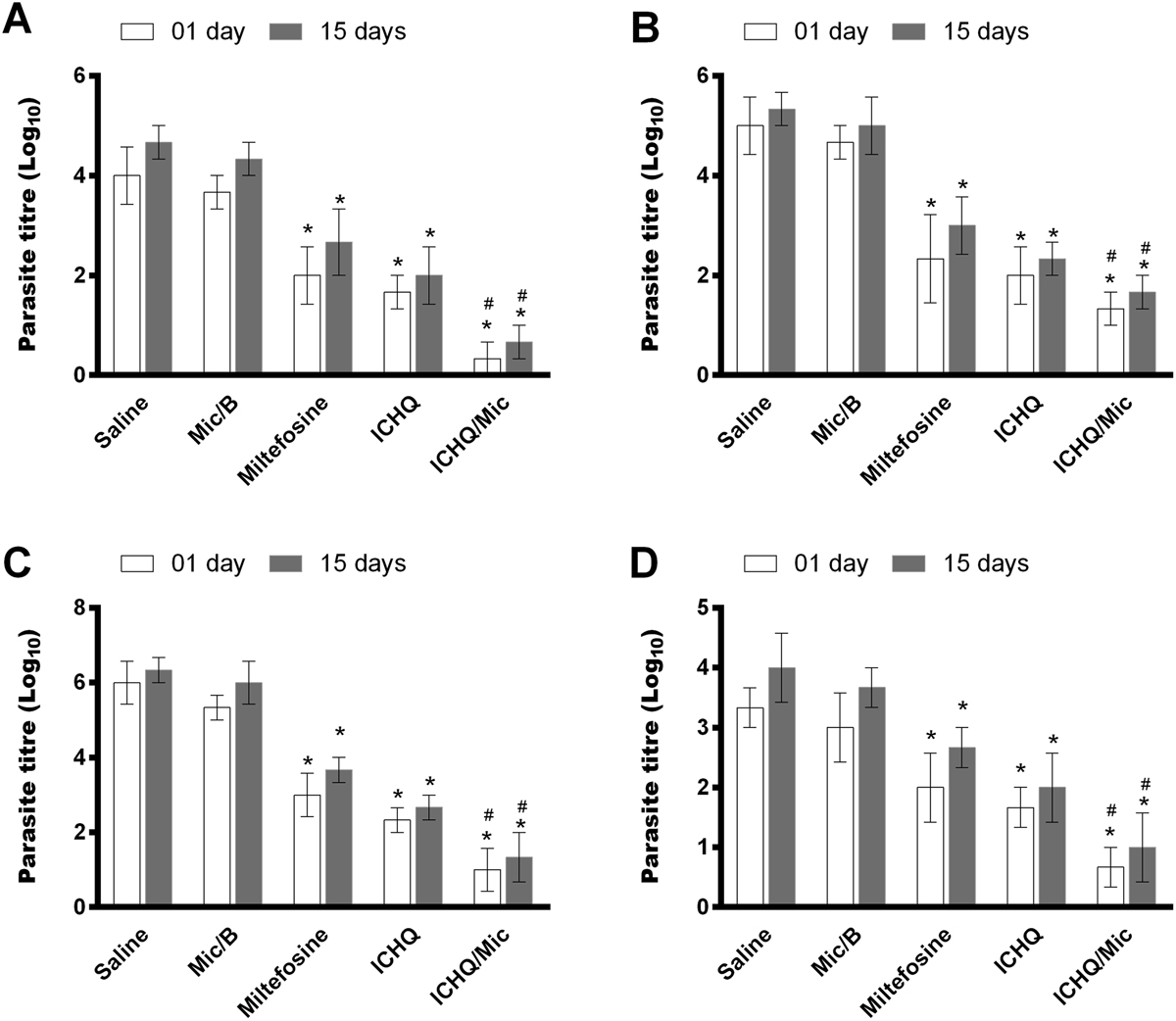
Parasite load evaluated by a limiting dilution assay. To evaluate the in vivo antileishmanial action of ICHQ incorporated or not in a micellar system, BALB/c mice (n = 12 per group) were subcutaneously infected with 107 Leishmania infantum stationary promastigotes. 45 days after infection, they received subcutaneous injections every 2 days for 10 days with: saline, empty micelle (Mic/B), ICHQ, ICHQ/Mic, or miltefosine (oral route). Half of the animals per group were euthanized one and 15 days after treatment, when liver, spleen, bone marrow and draining lymph nodes were collected for evaluation of the parasite load. White and grey bars indicate the mean ± standard deviation of the groups, one and 15 days after treatment, respectively, in liver (A), spleen (B), bone marrow (C), and draining lymph nodes (D). (*) indicates a statistically significant difference in relation to the saline and Mic/B groups (p < 0.001). (#) indicates a statistically significant difference in relation to the miltefosine and ICHQ groups (p < 0.01).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


