Figure 5
Download original image
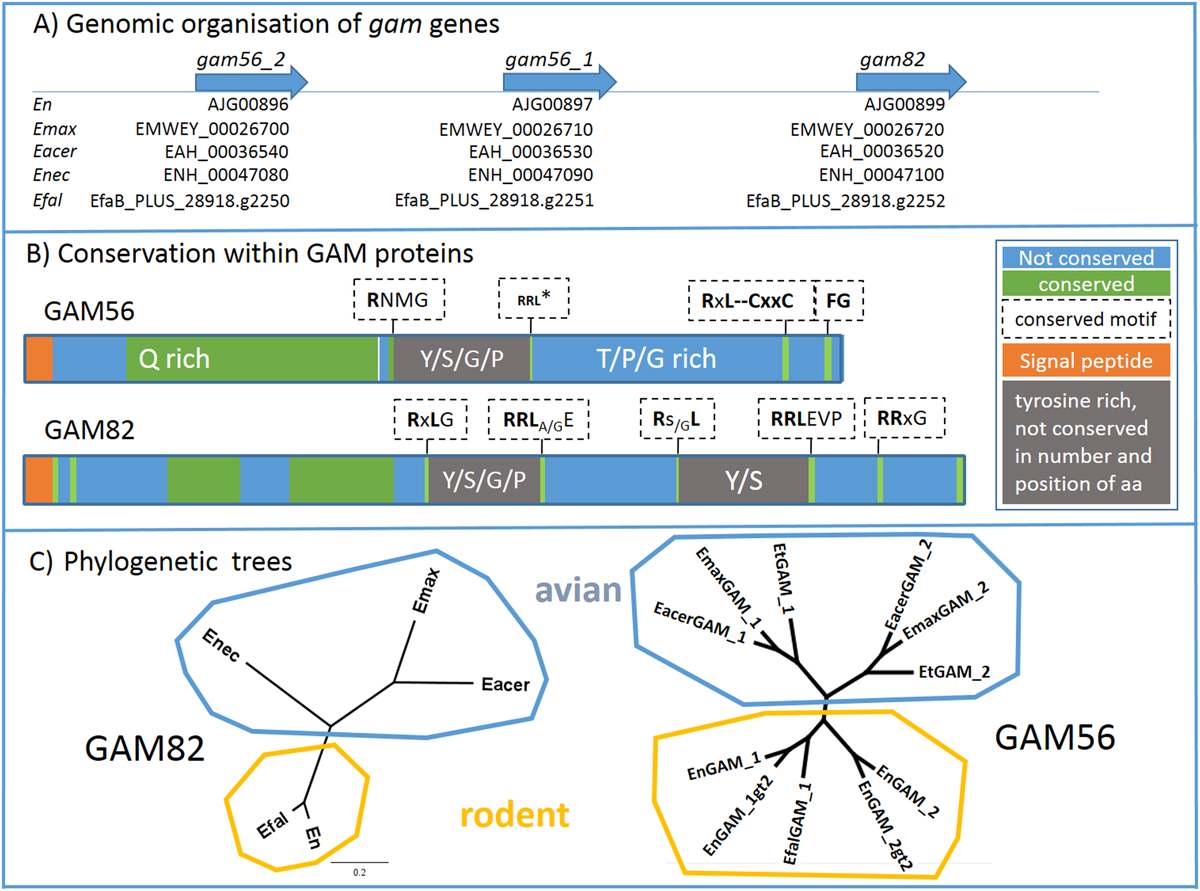
A) Clustered organisation of gam56 and gam82 orthologues. The gam genes are situated in a cluster in all investigated Eimeria species [GenBank ID: En (E. nieschulzi), ToxoDB-ID: Emax (E. maxima), Eacer (E. acervulina), Enec (E. necatrix), Efal (E. falciformis)].
B) Conservation within GAM proteins. The consensus structure of GAM56 and GAM82 proteins from different Eimeria species are based on the ClustalOmega alignment. RRL*: RRL motif is not conserved in Emax and Eacer GAM56_2, but in all other species and all GAM56_1 variants. (Complete alignment of GAM56 sequences in the SF1G, and H for the GAM82 alignment).
C) Phylogenetic trees show distribution of GAM82 and GAM56 in particular branches of rodent and avian Eimeria species. GAM82 shows larger distances in the avian branch than in the rodent branch, which confirms the close relationship of E. falciformis and E. nieschulzi. GAM56 branches within the avian Eimeria into two groups, GAM56_1 and GAM56_2, indicating that the common ancestor of this Eimeria species already had two GAM56 versions that evolved further in the particular Eimeria species.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


