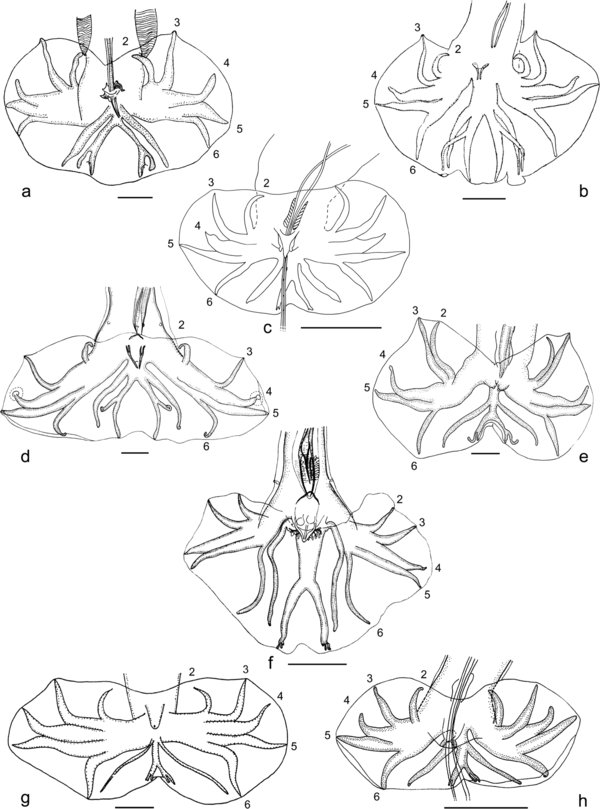
Fig. 3
Download original image
Figs. 3a-d
Basic patterns. Scale-bars: 50 μm.
a. Type 2-3. Rays 2 and 3 are grouped, arising first and together from the common trunk of rays 2 to 6; rays 4 to 6 have a common trunk and diverge at the same level. Ex: Paraheligmonella interrogans (Lent & Freitas, 1938). After Durette-Desset (1968b), modified.
b. Type 2-2-1. Rays 2 and 3 are grouped, arising first and together from the common trunk of rays 2 to 6; ray 6 arises at the same level as ray 3; rays 4 and 5 are the last to diverge. Ex: Heligmostrongylus crucifer (Travassos, 1943). After Travassos (1943), modified.
c. Type 1-3-1. Rays 2 and 6 arise first and at the same level from the common trunk of rays 2 to 6; rays 3 to 5 have a common trunk. Ex: Hypocristata tercera Durette-Desset & Guerrrero, 2006. In this case ray 3 diverges first from the common trunk of rays 3 to 5 in the right lobe and at the same level as ray 5 in the left lobe. After Durette-Desset & Guerrrero (2006), modified.
d. Type 1-4. Ray 2 arises first from the common trunk of rays 2 to 6; rays 3 to 6 have a long common trunk. Ex: Fuellebornema bocqueti (Durette-Desset, 1970a). In this case ray 3 diverges at the same level as ray 6 on the common trunk of rays 3 to 6. After Durette-Desset (1970a), modified.
Figs. 3e-h
Intermediary patterns. Scale-bars: 50 μm.
e. Type 2-3 t 2-2-1. Rays 2 and 3 are grouped, arising first and together from the common trunk of rays 2 to 6; rays 4 to 6 have a common trunk; ray 6 diverges close to the level of the divergence of ray 3 and proximally to that of rays 4 and 5. Ex: Neoheligmonella acomysi Durette-Desset & Gibson, 1990. In this case rays 2 and 3 are apposed for much of their length. After Durette-Desset & Gibson (1990), modified.
f. Type 2-2-1 t 1-3-1. Rays 2 and 6 arise first and at the same level from the common trunk of rays 2 to 6; rays 3 arise just distally to the level of divergence of rays 2 and 6; rays 4 and 5 are the last to diverge. Ex: Pudica pudica (Travassos, 1921). After Cassone & Durette-Desset (1991), modified.
g. Type 1-3-1 t 1-4. Rays 2 arise first from the common trunk of rays 2 to 6; rays 6 arise slightly distally to the level of divergence of rays 2 and proximally to that of rays 3; rays 3 to 6 have a short common trunk. Ex: Spalacina yanchevi Biserkov, Durette-Desset & Genov, 1995. After Biserkov et al. (1995), modified.
h. Type 2-2-1 t 1-4. Rays 2 arise first from the common trunk of rays 2 to 6; rays 3-6 have a short common trunk; rays 6 arise at the same level as rays 3; rays 4 and 5 are the last to diverge. Ex: Hypocristata anguillula (Durette-Desset, 1971). Ray 3 is still grouped with ray 2 since its extremity supports the ventral lobe. After Durette-Desset (1971), modified.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


